[IMID 2017] Opening solution for next generation high-resolution OLED implementation
Various solutions for high resolution OLED implementation were released at iMiD 2017 held in COEX from October 18th to 19th. As the resolution of small and mid-sized OLEDs, which are currently being commercialized, is staying at the QHD level, the solutions released at this time have attracted a great deal of attention from display members.
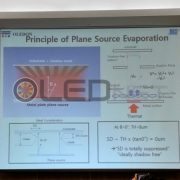
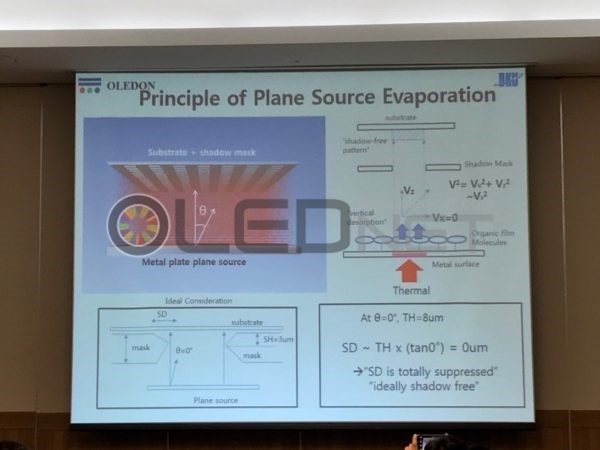
First, Hwang Chang-hoon, CEO of OLEDON, who is developing plane source FMM deposition technology, announced at the business forum, “The plane source FMM deposition technology currently being developed is the only alternative for ultra-high resolution OLED manufacturing at 2,250 ppi”. Hwang Chang-hoon CEO said, “We measured the shadow distance using a-step, and it was 0.38 μm. We can fabricate OLED device with 2,250 ppi only if we have this shadow distance.” “We are currently looking for shadow-free process conditions”

<Difference in shadow distance between point source and plane source>
In addition, Hwang Chang-hoon said, “We first co-deposited the host material and the dopant material on the metal plate to evaporate the deposited green donor thin film and measure the green target thin film with the same PL wavelength for the first time” and “Color control of target thin films made with plate sources can be controlled by the amount of dopant molecules in the donor film, so color control is expected to be easy”.
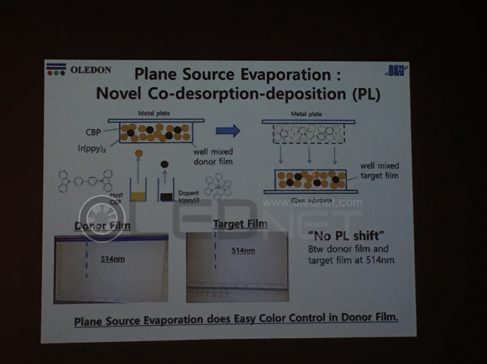
<OLEDON plane evaporation co-deposition material>
AP Systems, which recently announced the successful development of 1,000 ppi FMM using ultra-short pulse laser (USPL), exhibited 5.28 inch FMM of 825 ppi and 4.72 inch FMM of 677 ppi at this exhibition. A company official said, “By developing a burr-free laser process to solve the burr problem caused by the heat generated during the fabrication process, it is possible to fabricate not only FMM of 1170 ppi but also FMM of various shapes”.

<5.28 inch 825ppi FMM of AP Systems>
Finally, Philoptics unveiled FMMs fabricated using electro forming, especially, FMM of 1,200 ppi, which attracted attention this time, was displayed separately in the VIP room. A company official said “We have secured the stability of the process for the production of 1,200 ppi FMM,” and mentioned “We plan to deliver it to panel makers for testing in the first half of next year, and aim to develop FMM at 2,000 ppi later.”

<FMM of Philoptics manufactured by electro forming method>
As such, in this iMiD 2017, various solutions for high-resolution patterning of OLEDs has been released. Recently, as the number of contents requiring high-resolution OLED such as virtual reality contents increases, interest of smartphone users are increasingly interested. It is worth noting which solution will enable the small to medium-sized UHD OLED era.