A Korean venture company has succeeded in developing blue dopant for Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLED) that a Japanese company has had its exclusive patent for. The dopant is an element that improves efficiency and life time by mixing with host that actually colors within the OLED.
In the meantime, many domestic material companies have developed OLED host, but it is the first case that a venture company has independently developed dopant on a commercial scale without receiving any support of large corporations.
Material Science (CEO Lee Soon-chang), an organic material developer for OLED has developed a technology that can replace Japanese I Company’s patent for blue dopant. Established in 2014, Material Science is supplying HTL( Hole Transporting Layer) and ETL (Electron Transfer Layer) to OLED panel makers.
Half of the 50 employees are R&D personnel. Last year, its sales were 6.6 billion won, and it is expected to exceed 10 billion won this year.
This time, due to the development of blue dopant by Material Science, OLED panel companies have an alternative to supply blue host and dopant besides I Company.
Japanese I Company has been developing blue dopant since 1995. At present, the company has more than 30 patents related to blue dopant (based on Japanese application for a patent), and its major 8 patents are valid until 2034. In particular, it has an exclusive patent for the combination method of blue dopant that includes blue host and pyrene with an anthracene structure (a compound in which three benzene rings are sequentially bonded). For this reason, the panel makers which purchase dopant from I Company must buy its host. If they mix I Company’s blue dopant with another company’s host, it is inevitable to infringe the patent in the case a host material has an anthracene skeleton.
Both Samsung Display and LG Display have been using I Company’s blue dopant and host.
The blue dopant developed by Material Science is designed to make molecules that are completely out of I Company’s compound patent. Conventionally, the method of applying an electron acceptor to a molecule has been used to improve the efficiency and lifetime of OLED and have a blue color.
On the other hand, Material Science introduces electron donor into molecules to improve the efficiency and lifetime while generating dark blue color. This dopant greatly reduces the solvent-dependent color development (solvatochromism) where emission wavelength changes due to the polarity of the surroundings. Therefore, the change of emission wavelength is also greatly reduced.
Jung Jae-ho, a researcher at Material Science said, “We have developed a new structure and a synthesis method, which makes it possible to produce its differentiated dopant.” “Panel companies are now able to utilize various types of blue hosts”. In addition, Material Sciences has been recently developing TADF(Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence) that OLED panel makers are struggling to introduce for the longer life of blue-emitting phosphors.
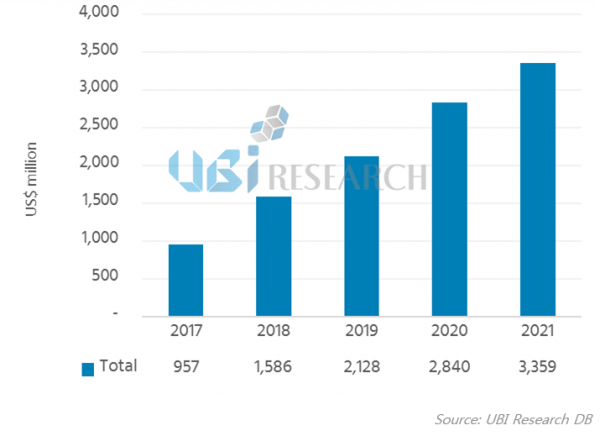
<OLED emitting material market forecast, UBi Research>
According to UBi Research, the OLED organic market is expected to reach $ 3.36 billion by 2021 (about 3.8 trillion won). And blue materials account for 11.5% of total sales.


